128-13-2
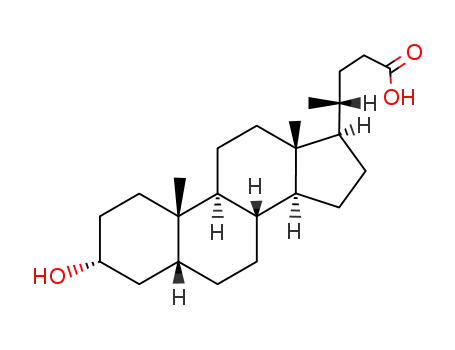
- Product Name:Ursodeoxycholic Acid
- Molecular Formula:C24H40O4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:392.579
Product Details;
CasNo: 128-13-2
Molecular Formula: C24H40O4
Appearance: white crystalline powder
Chinese Factory Supply Ursodeoxycholic Acid, Offer 128-13-2 Efficient Shipping
- Molecular Formula:C24H40O4
- Molecular Weight:392.579
- Appearance/Colour:white crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:0mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:203-204 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:60.5 ° (C=2, EtOH)
- Boiling Point:547.1 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 5.04±0.04(H2O t = 25.0±0.1 I = 0.00)(Approximate)
- Flash Point:298.8 °C
- PSA:77.76000
- Density:1.128 g/cm3
- LogP:4.47790
Ursodeoxycholic acid(Cas 128-13-2) Usage
|
Choleretic drugs |
Ursodeoxycholic acid is a chemical agent of natural bile acid which is isolated from the bile of bear. It is the stereo-isomer of chenodeoxycholic acid. It has a similar litholysis effect, efficacy as chenodeoxycholic acid. However, it has a short course of treatment and a small dose. It is bound with taurine in the bile in vivo, and is a hydrophilic bile acids as well as a dissolving agent of cholesterol. It can reduce the secretion of cholesterol in the liver, lower the saturation content of cholesterol in bile, promote the secretion of bile acids, and increase the solubility of cholesterol in the bile so that cholesterol gallstones can be dissolved or prevented. Moreover, it can increase the secretion amount of bile, and have a choleretic effect by relaxing the bile duct mouth sphincter which smoothen the discharge of calculus. This product, however, cannot dissolve other types of gallstones. Ursodeoxycholic acid is useful in the treatment of cholesterol stones, hyperlipidemia, bile secretion disorders, primary biliary cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, bile reflux gastritis and prevention of liver allograft rejection and reaction. The calculus-dissolving effect of this product is slightly weaker than the CDCA.ursodeoxycholic acid structure |
|
Pharmacological effects |
Ursodeoxycholic acid, namely 3α, 7 β-dihydroxy bile acid, is the 7β-hydroxy epimer of chenodeoxycholic acid. Because of this small structural difference, the product is hydrophilic. It can reduce the activity of the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis in the liver--β-hydroxyl-β-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, thus inhibiting the cholesterol synthesis. It also forms a stable liquid crystalline suspension with cholesterol, and thus unsaturated the bile cholesterol, thereby promoting the separation and dissolution of cholesterol stone. This product can also inhibit the intestinal absorption of cholesterol. Ursodeoxycholic acid can also antagonize the cytotoxic effects of endogenous hydrophobic bile acids, protecting the liver cell membrane. By reducing the overexpression of the main membrane tissue compatibility antigen MHC-1, it can inhibit the production of interleukin-2,4, tumor necrosis factor and interferon α; and increasing the body's levels of interleukin-10,12; It also directly binds to the glucocorticoid receptor, playing a role in immune regulation. In addition, Ursodeoxycholic acid can also inhibit apoptosis, inhibit inflammation, scavenge free radical and have antioxidant effects. After oral administration, it is absorbed through non-ionic passive diffusion in the jejunum, and through active transport in the ileum. The effect of first-pass is large, 50% to 75% of the orally administrated dose is uptake by liver. It is mainly distributed in the liver, intestines and blood plasma, and has a 96% to 99% plasma protein binding rate. Ursodeoxycholic acid concentration in the bile exhibit dose-dependent increase; upon a dose of 20~30mg/(kg ? d), its concentration in bile is over 60%, reaching the best therapeutic effect. It binds to glycine, taurine in the liver, and is metabolized by intestinal. A small part of metabolite product is excreted from by urine, mostly by the fecal excretion. Biological half-life of oral administration is 3.5 to 5.8 days. |
|
Drug Interactions |
(1) In combination with chenodeoxycholic acid, the effect of promoting cholesterol level and de-saturation in bile were more than single drugs. The effect is also greater than that of the sum of the two drugs. (2) This product is not suitable taken together with cholestyramine or antacids containing aluminum hydroxide for not affecting the absorption. (3) Oral contraceptives may affect the efficacy of the product. |
|
Side effects |
Ursodeoxycholic acid has a small side effects than chenodeoxycholic acid. It generally doesn’t cause diarrhea. Occasional occurrence of constipation, allergies, headaches, dizziness, pancreatitis, and tachycardia. |
|
Precautions |
(1) For elderly patients, apply with caution. (2) Long-term use can increase the number of peripheral platelet. (3) If biliary colic occurs recurrently during the treatment of cholesterol gallstones and the symptoms are not alleviated or even become worse or clear stones calcification happen, stop the treatment and apply surgery. (4) This product cannot used to dissolve bile pigment stones, mixed stones and stones cannot be penetrated by X-ray. (5) Check liver function regularly during the treatment. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White powder; odorless, bitter taste. M.p.: 200-204 °C. Highly soluble in ethanol and glacial acetic acid, soluble in sodium hydroxide solution but insoluble in chloroform. UDCA is the isomer of CDCA, which has stronger stone-dissolving effect than CDCA and cause no diarrhea and liver toxicity. UDCA can reduce the absorption of cholesterol, and can reduce the synthesis of cholesterol and the level of cholesterol in bile. In addition, UDCA can also reduce the concanavalin A-binding fragment. |
|
Uses |
Ursodeoxycholic acid is a naturally occurring bile salt in humans. It is rapidly absorbed in the small intestine and excreted with the bile. Ursodeoxycholic acid is the drug of choise for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosis cholanyitis. The daily dose amounts to 10-15 mg/kg. It has no side effects even after a treatment period of up to 20 years.Dissolution of gallstones. Mainly used for the treatment of inoperable cholesterol gallstones, it will have a cure rate especially in the case when gallbladder is basically normal, stones have a 15mm or lower diameters, X-ray penetrable, non-calcified and high-floating cholesterol stones.Ursodeoxycholic acid can also improve the efficacy of α-interferon on treatment of chronic hepatitis C. It can also used to treat diarrhea, rare constipation, allergic reactions, itching, headache, dizziness, stomach pain, pancreatitis and bradycardia Patients of completely biliary obstruction or severe liver dysfunction and pregnant women should avoid using. Dissolution of gallstonesUrsodeoxycholic acid or ursodiol is a naturally occurring bile acid that is used dissolve cholesterol gall stones and to treat cholestatic forms of liver diseases including primary biliary cirrhosis. |
|
Originator |
Actigall,Novartis |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Ursodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid found in the bile of bears (Ursidae) as a conjugate with taurine. Used therapeutically, it prevents the synthesis and absorption of cholesterol and can lead to the dissolution of gallstones. It has a role as a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a bile acid, a dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid and a C24-steroid. It is a conjugate acid of an ursodeoxycholate. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
Chenodeoxycholanic acid was dissolved in acetic acid and to this solution aqueous solution of CrO3 was added. As a result 3,7-diketodeoxycholanic acid was obtained, yield 95%, melting point 145°C. 15.0 g of 3,7-diketodeoxycholanic acid were dissolved in 80 ml of toluene, then petroleum ether 30 ml were added. 3,7-Diketodeoxycholanic acid as an oil precipitate was obtained, melting point 152°-154°C. 10.0 g of 3,7-diketodeoxycholanic acid were dissolved in 300 ml butanol, heated to 120°-130°C on bath and then sodium metallic 13.0 g were added. After that to this mixture hydrochloric acid was added for neutralization. Ursodeoxychlolanic acid was obtained, yield 9.4 g, melting point 193°C (recrystallization from ethyl acetate). |
|
Brand name |
Actigall (Watson); Urso (Axcan Scandipharm). |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Gallostone dissolving agent, Hepatoprotectant |
|
General Description |
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a secondary bile acid that helps regulate cholesterol. Mass spectrometry-based analysis of UDCA is routinely performed in clinical diagnostic testing applications such as neonatal testing of inborn errors of bile acid synthesis, differentiating among types of familial intrahepatic cholestasis, and therapeutic monitoring of patient responses to UDCA therapy. This Certified Spiking Solution? is suitable as a starting material in preparation of linearity standards, calibrators, and controls for use in LC-MS/MS and GC/MS bile acid testing methods. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Ciclosporin: unpredictably increases the absorption of ciclosporin in some patients. |
|
Metabolism |
Ursodeoxycholic acid is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes enterohepatic recycling. It is partly conjugated in the liver before being excreted into the bile. Under the influence of intestinal bacteria the free and conjugated forms undergo 7α-dehydroxylation to lithocholic acid, some of which is excreted directly in the faeces and the rest absorbed and mainly conjugated and sulphated by the liver before excretion in the faeces. |
|
Purification Methods |
Recrystallise ursodiol from wet Et2O, EtOH or EtOH/MeOH. [Iwasaki Hoppe Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 244 181, 183 1936, Beilstein 10 III 1635.] |
InChI:InChI=1/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-7-21(27)28)17-5-6-18-22-19(9-11-24(17,18)3)23(2)10-8-16(25)12-15(23)13-20(22)26/h14-20,22,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/p-1/t14-,15-,16-,17-,18+,19+,20+,22+,23+,24-/m1/s1
128-13-2 Relevant articles
Novel FXR (farnesoid X receptor) modulators: Potential therapies for cholesterol gallstone disease
Yu, Donna D.,Andrali, Sreenath S.,Li, Hongzhi,Lin, Min,Huang, Wendong,Forman, Barry M.
, p. 3986 - 3993 (2016)
Metabolic disorders such as diabetes are...
Fluorescent Sensors for Molecules Guest-Responsive Monomer and Excimer Fluorescence of 6A,6B-; 6A,6C-; 6A,6D-; and 6A,6E-Bis(2-naphthylsulfonyl)-γ-cyclodextrins
Hamada, Fumio,Minato, Shingo,Osa, Tetsuo,Ueno, Akihiko
, p. 1339 - 1346 (1997)
Flexible hosts, 6A,6B-; 6A,6C-; 6A,6D-; ...
Regioselective oxidation of cholic acid and its 7β epimer by using o-iodoxybenzoic acid
Dangate, Prasad S.,Salunke, Chetan L.,Akamanchi, Krishnacharya G.
, p. 1397 - 1399 (2011)
Rational exploration directed by DFT (de...
7α- and 12α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus lwoffii: a new integrated chemo-enzymatic route to ursodeoxycholic acid
Giovannini, Pier Paolo,Grandini, Alessandro,Perrone, Daniela,Pedrini, Paola,Fantin, Giancarlo,Fogagnolo, Marco
, p. 1385 - 1390 (2008)
We report the very efficient biotransfor...
Engineering Regioselectivity of a P450 Monooxygenase Enables the Synthesis of Ursodeoxycholic Acid via 7β-Hydroxylation of Lithocholic Acid
Grobe, Sascha,Badenhorst, Christoffel P. S.,Bayer, Thomas,Hamnevik, Emil,Wu, Shuke,Grathwol, Christoph W.,Link, Andreas,Koban, Sven,Brundiek, Henrike,Gro?johann, Beatrice,Bornscheuer, Uwe T.
, p. 753 - 757 (2021)
We engineered the cytochrome P450 monoox...
Two-step enzymatic synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid with a new 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Ruminococcus torques
Zheng, Ming-Min,Wang, Ru-Feng,Li, Chun-Xiu,Xu, Jian-He
, p. 598 - 604 (2015)
7β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7β-HSDH...
7α-OH epimerisation of bile acids via oxido-reduction with Xanthomonas maltophilia
Medici, Alessandro,Pedrini, Paola,Bianchini, Ercolina,Fantin, Giancarlo,Guerrini, Alessandra,Natalini, Benedetto,Pellicciari, Roberto
, p. 51 - 56 (2002)
The microbial 7α-OH epimerisation of cho...
Hydroxylation of lithocholic acid by selected actinobacteria and filamentous fungi
Kollerov,Monti,Deshcherevskaya,Lobastova,Ferrandi,Larovere,Gulevskaya,Riva,Donova
, p. 370 - 378 (2013)
Selected actinobacteria and filamentous ...
A Facile Route to Ursodeoxycholic Acid Based on Stereocontrolled Conversion and Aggregation Behavior Research
Dou, Qian,Jiang, Zhongliang
, p. 588 - 594 (2016)
A facile route to ursodeoxycholic acid (...
Continuous Production of Ursodeoxycholic Acid by Using Two Cascade Reactors with Co-immobilized Enzymes
Zheng, Ming-Min,Chen, Fei-Fei,Li, Hao,Li, Chun-Xiu,Xu, Jian-He
, p. 347 - 353 (2018)
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is an effect...
Synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid from plant-source (20S)-21-hydroxy-20-methylpregn-4-en-3-one
Gu, Xiang-Zhong,He, Li-Ming,Li, Chen-Chen,Qiu, Wen-Wei,Wang, Jie
, (2020)
A novel synthetic route of producing urs...
Flavin Oxidoreductase-Mediated Regeneration of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide with Dioxygen and Catalytic Amount of Flavin Mononucleotide for One-Pot Multi-Enzymatic Preparation of Ursodeoxycholic Acid
Chen, Xi,Cui, Yunfeng,Feng, Jinhui,Wang, Yu,Liu, Xiangtao,Wu, Qiaqing,Zhu, Dunming,Ma, Yanhe
, p. 2497 - 2504 (2019)
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), a pharmaceu...
STEREOCHEMISTRY OF REDUCTION OF CYCLIC KETONES BY ALKALI METALS AND BY SODIUM DITHIONITE.
Castaldi, Graziano,Perdoncin, Giulio,Giordano, Claudio
, p. 2487 - 2490 (1983)
An opposite stereoselectivity is observe...
128-13-2 Process route
-
- 434-13-9
Lithocholic acid

-
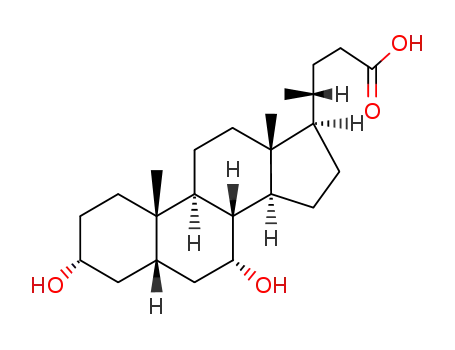
- 474-25-9
chenodeoxycholic acid

-
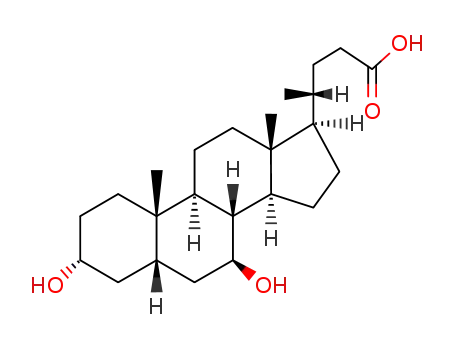
- 128-13-2
ursodeoxycholic acid

-
- 911-40-0
7-ketodeoxycholic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With Lentzea waywayandensis VKM Ac-1970; In methanol; aq. phosphate buffer; pH=7; Microbiological reaction;
|
-
![[3H] Sodium glycoursodeoxycholate](/upload/2023/9/6db5bb0b-8999-4039-8097-bfcc1f281c8f.png)
- 92411-07-9
[3H] Sodium glycoursodeoxycholate

-

- 128-13-2
ursodeoxycholic acid

-
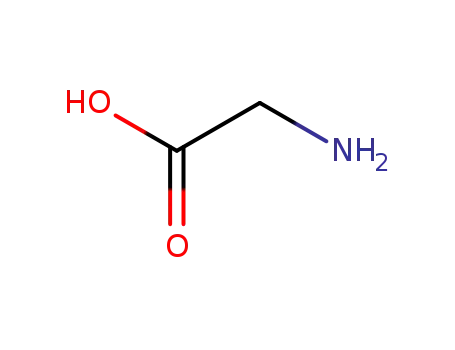
- 56-40-6,18875-39-3,25718-94-9
glycine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With chloylglycine hydrolase; In phosphate buffer; at 84 ℃; for 0.0833333h;
|
128-13-2 Upstream products
-
859-97-2
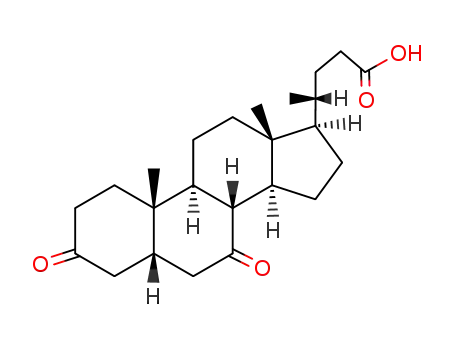
3,7-diketocholanic acid
-
4651-67-6
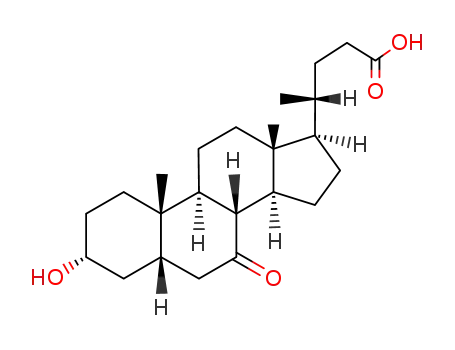
7-Ketolithocholic acid
-
141-52-6
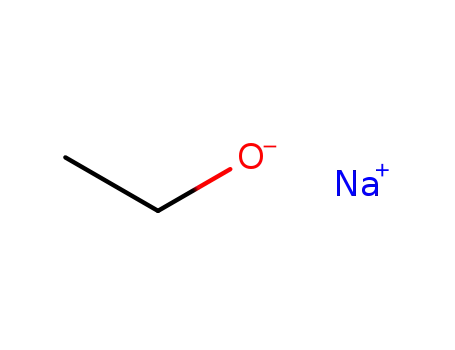
sodium ethanolate
-
555-31-7
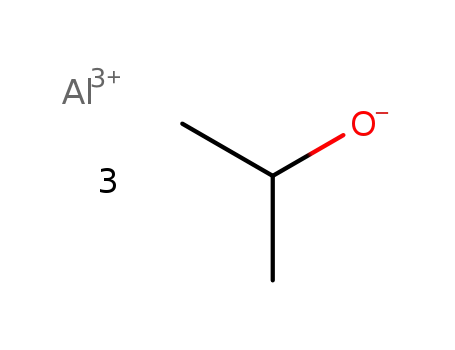
aluminum isopropoxide
128-13-2 Downstream products
-
88165-77-9
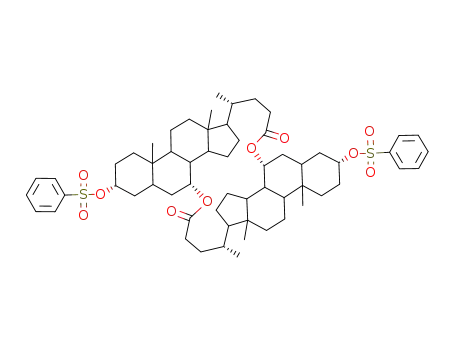
bis(3α-phenylsulfonyloxy-5β-cholansaeure-7α-yl)diester
-
92054-20-1
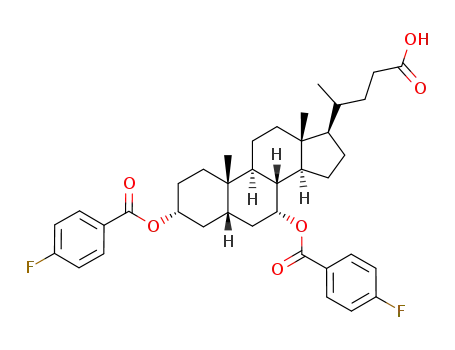
5β-cholanic acid-3α,7α-diol di-p-fluorobenzoate
-
10538-55-3
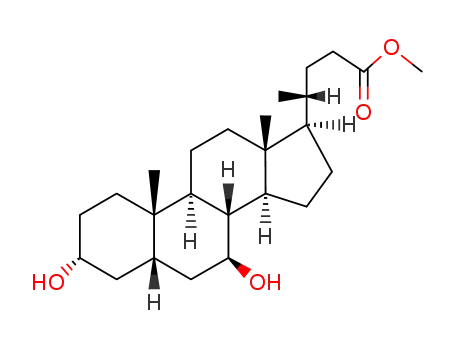
3α,7β-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid methyl ester
-
6159-50-8
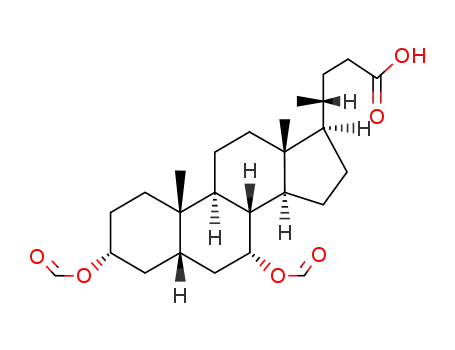
3α,7α-diformyloxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid
Relevant Products
-
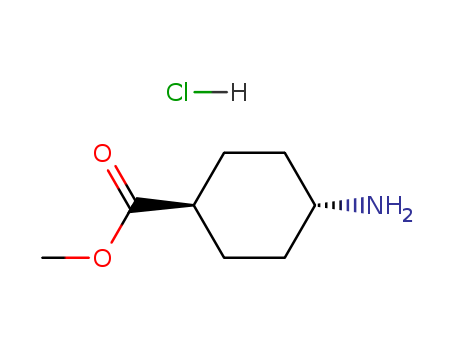
Methyl trans-4-aminocyclohexanecarboxylate hydrochloride
CAS:61367-07-5
-
tert-Butyl (trans-4-hydroxymethylcyclohexylmethyl)carbamate
CAS:172348-63-9
-
Capecitabine
CAS:154361-50-9